Introduction for MHA
The development of single-cell RNA (scRNA-seq) and spatial transcriptome sequencing (stRNA-seq) technologies has enabled the study of tissue and organ microenvironment heterogeneity at the molecular level and single-cell scale. Currently, scRNA data for nearly all human tissues and organs, as well as model animals (mice), have been published. However, in-depth analysis of these data often requires a foundation in bioinformatics, and the complex computational processes involved can hinder researchers from quickly retrieving the needed information. Moreover, some comprehensive scRNA databases do not specifically focus on the male genitourinary system and may suffer from issues such as irregular disease classification and cell clustering. To address these challenges, we present MHA, an online visual interactive website that provides scRNA and stRNA data for various tissues and organs of the male genitourinary system under both physiological and pathological conditions.
Overview for MHA
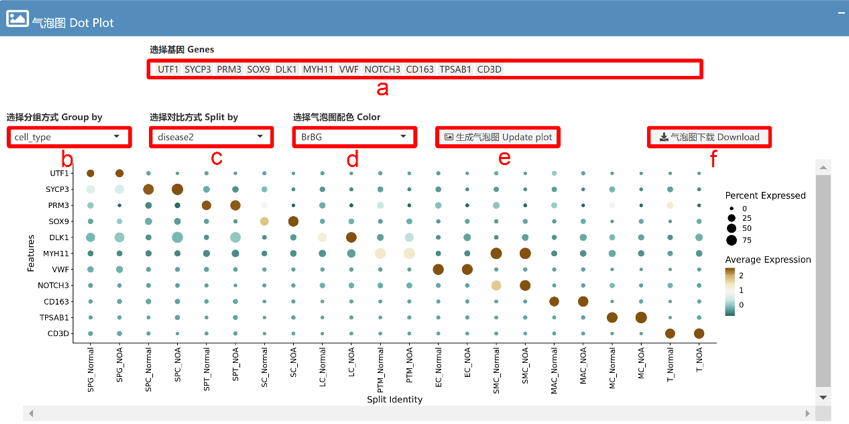
We focus on scRNA data related to the development and disease of the male genitourinary system. In the current version, MHA includes 12 datasets spanning 3 species (Homo sapiens, Rattus norvegicus, and Mus musculus) and 5 organs/tissues (Testis, Epididymis, Vas deferens, Corpus cavernosum, and Prostate), totaling 474,486 scRNA data points. Additionally, MHA provides two stRNA datasets for human and rat corpus cavernosum. For data visualization, we offer various output options, including UMAP and TSNE plots, violin plots, frequency bar plots, and bubble plots, to meet the diverse display needs of users.
scRNA datasets:
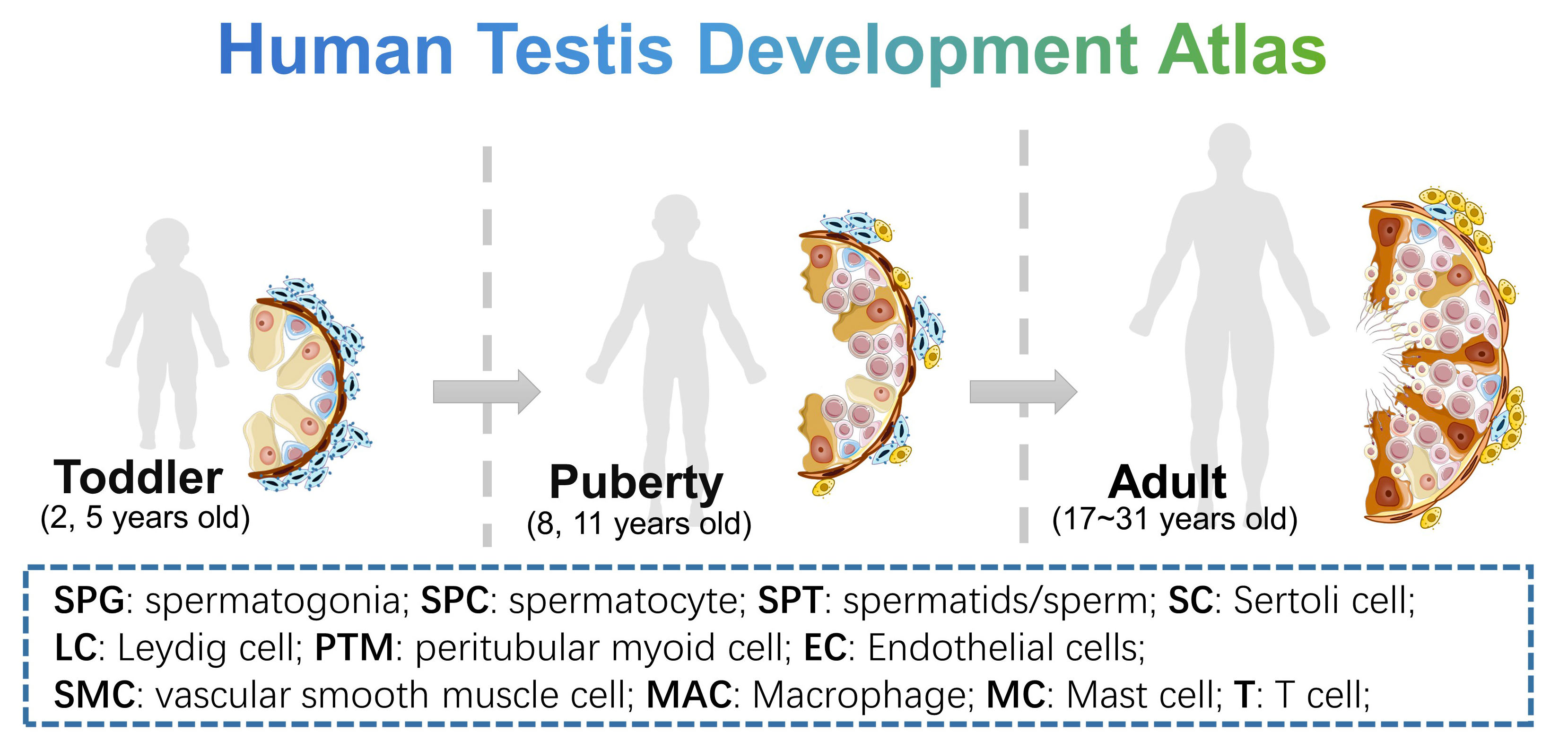
- Human Testis Development Atlas: 10 human testicular samples include 2 yo (n=1), 5 yo (n=1), 8 yo (n=1), 11 yo (n=1), 17 yo (n=1) and adults (n=5), to show the normal development process of human testis. Data could be downloaded from GSE149512 of GEO data base.
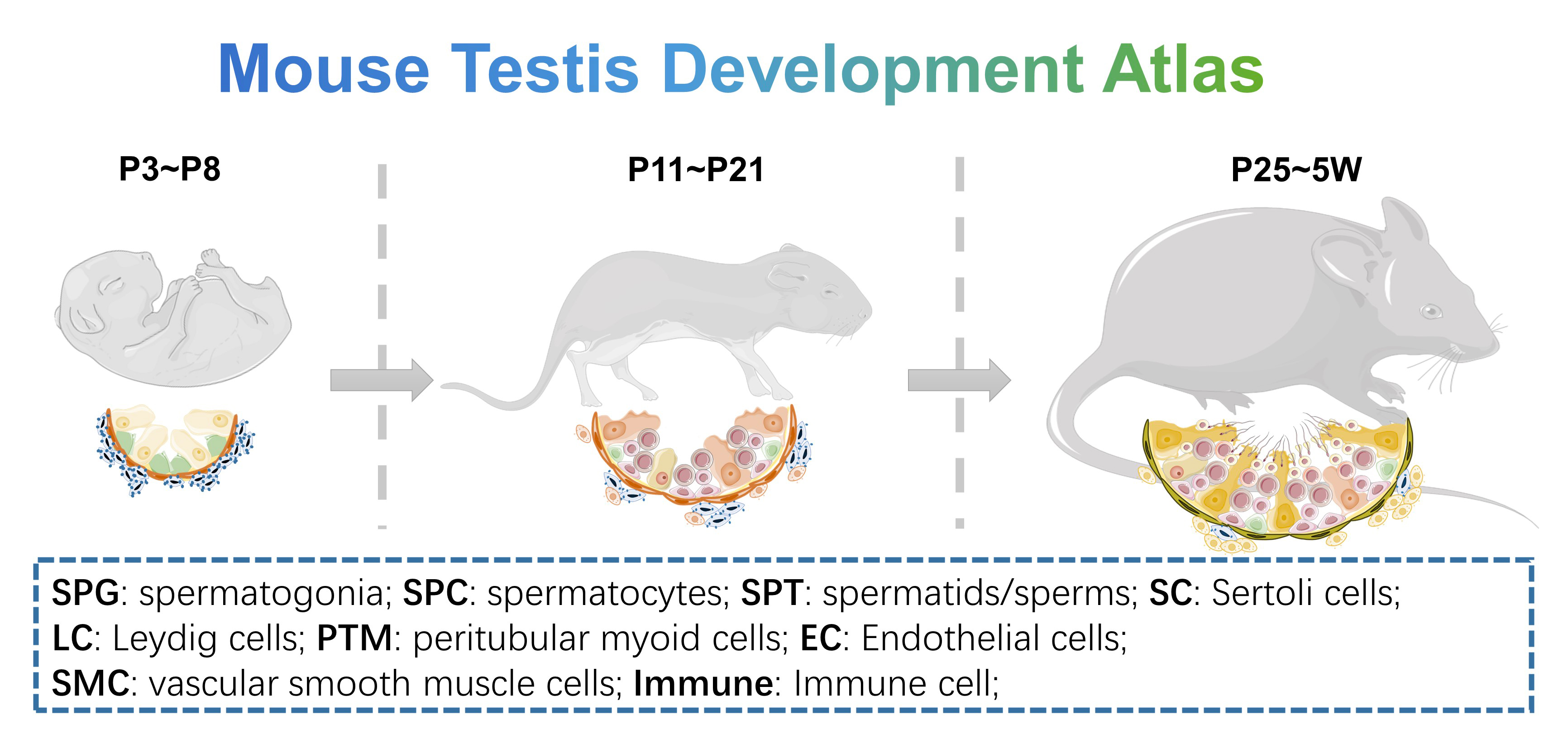
- Mouse Testis Development Atlas: 9 C57-mice testicular samples include 3 days (n=1), 6 days (n=1), 8 days (n=1), 11 days (n=1), 14 days (n=1), 17 days (n=1), 21 days (n=1), 25 days (n=1) and 5 weeks (n=1), to show the normal development process of mouse testis. Data could be downloaded from GSE211115 of GEO data base.
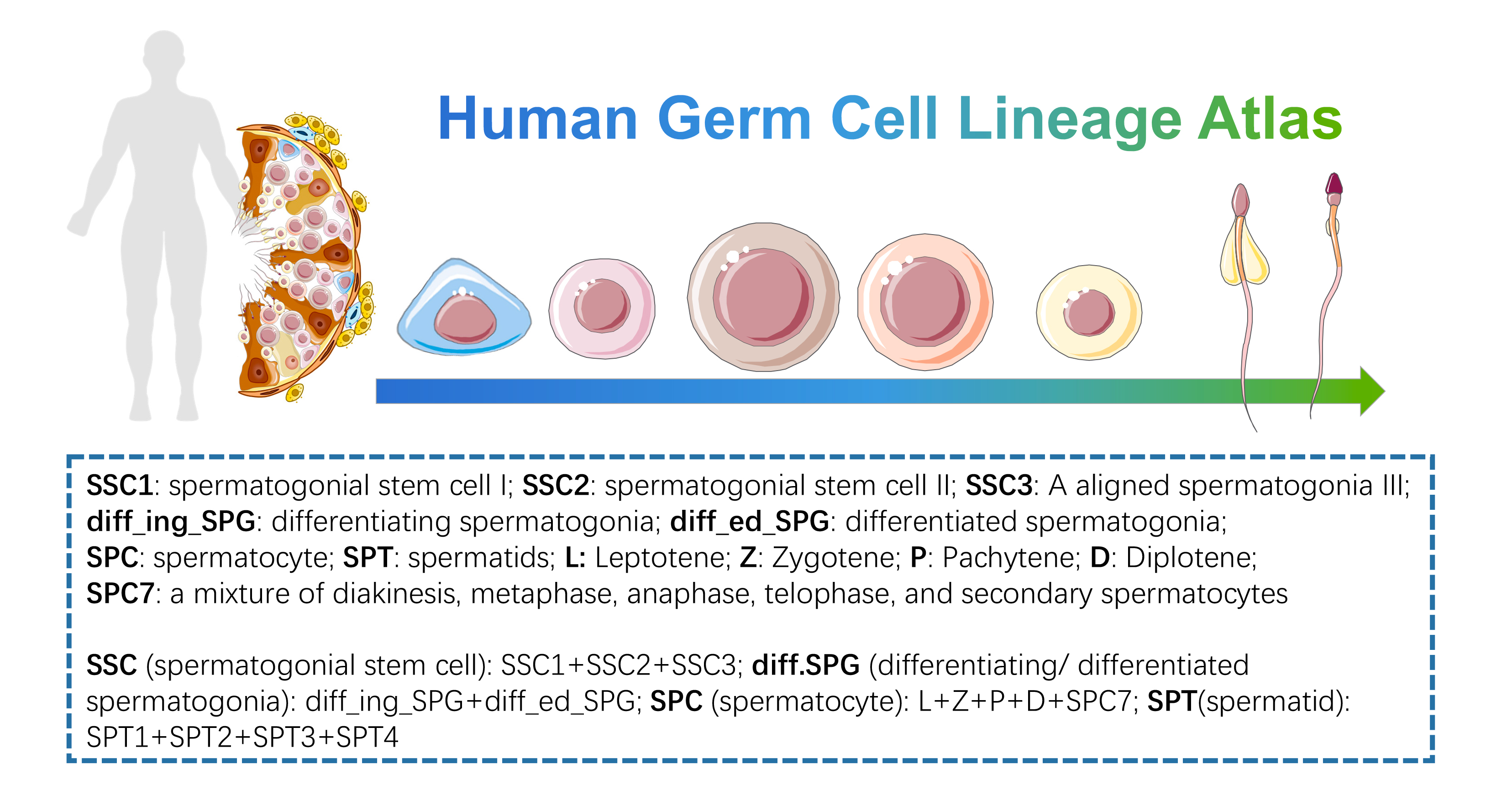
- Human Germ Cell Lineage Atlas: this dataset is the germ cell line subset of “Human Testis Development Atlas”, from spermatogonial stem cell to spermatid, we provide simple and detailed clustering classifications. Data could be downloaded from GSE149512 of GEO data base.
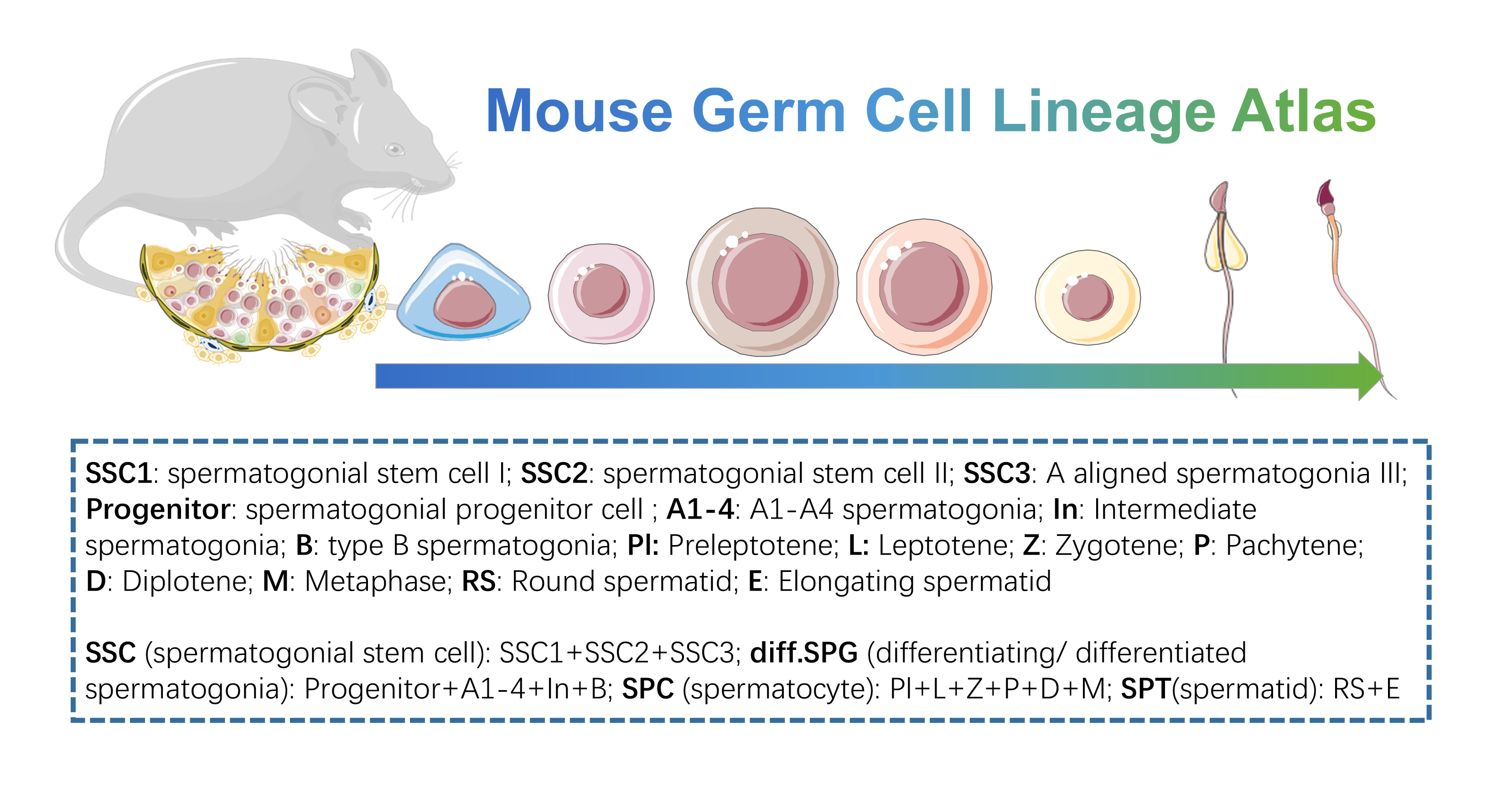
- Mouse Germ Cell Lineage Atlas: this dataset is the germ cell line subset of “Mouse Testis Development Atlas”, from spermatogonial stem cell to spermatid, we provide simple and detailed clustering classifications. Data could be downloaded from GSE211115 of GEO data base.
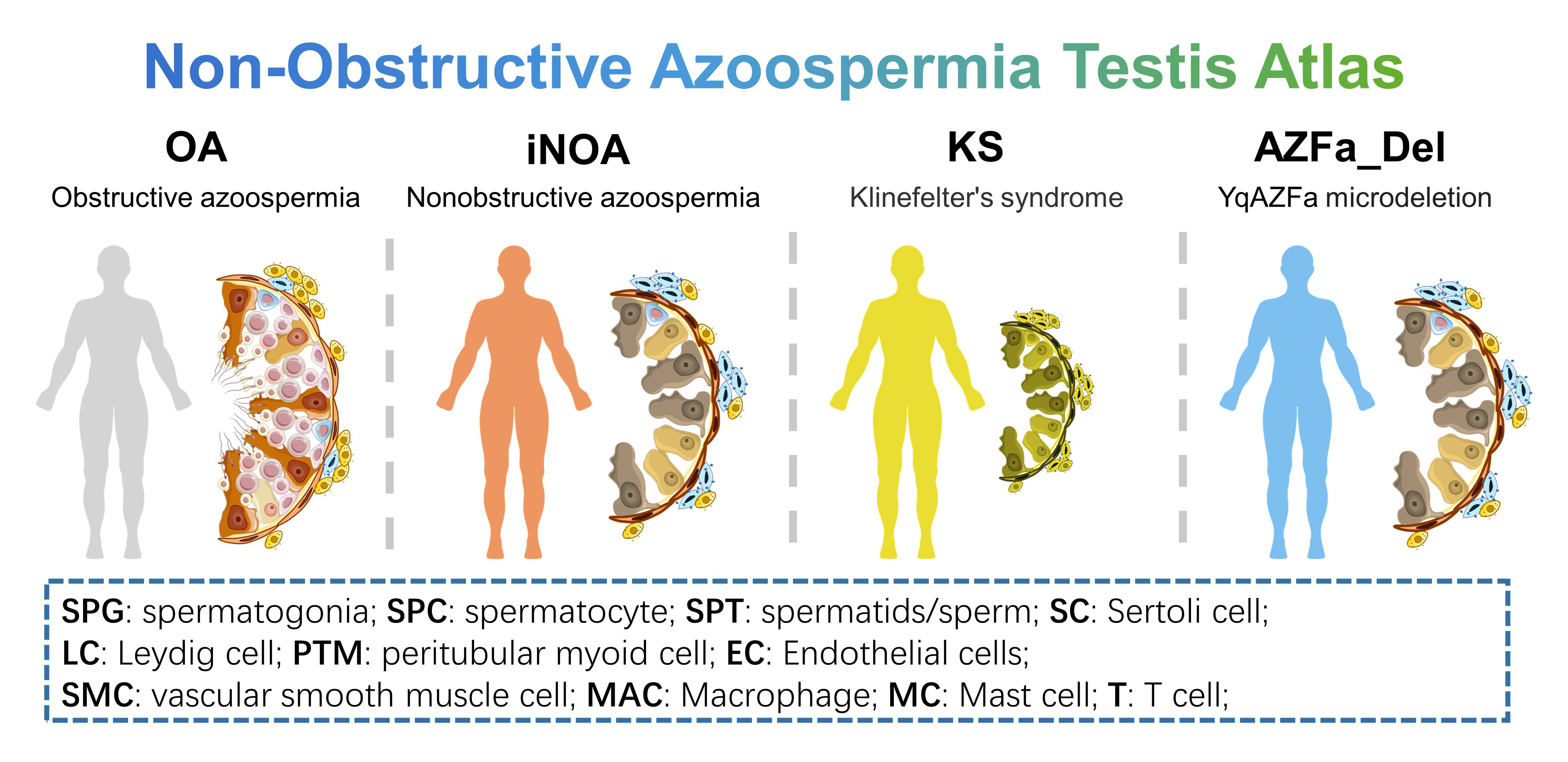
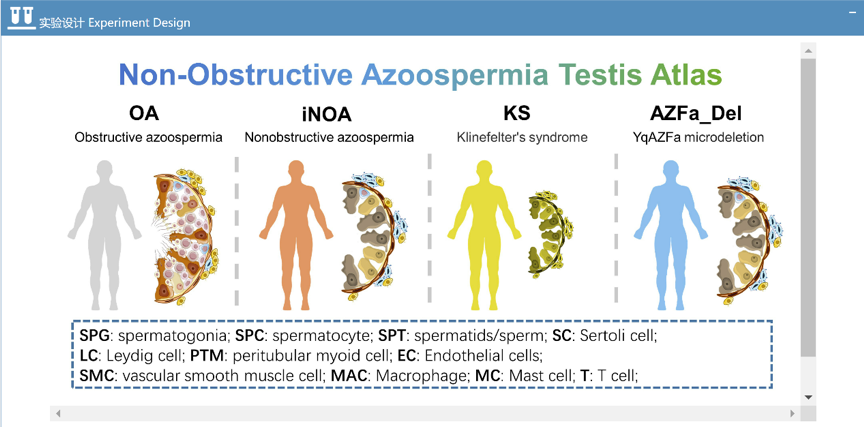
- Human Testis Non-Obstructive Azoospermia Atlas: this dataset included 5 adult testicular samples with normal spermatogenesis and 7 testicular samples of non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA). NOA can be further classified as idiopathic nonobstructive azoospermia (n=3), Klinefelter's syndrome (n=3) and YqAZFa microdeletion (n=1) according to etiology. Data could be downloaded from GSE149512 of GEO data base.
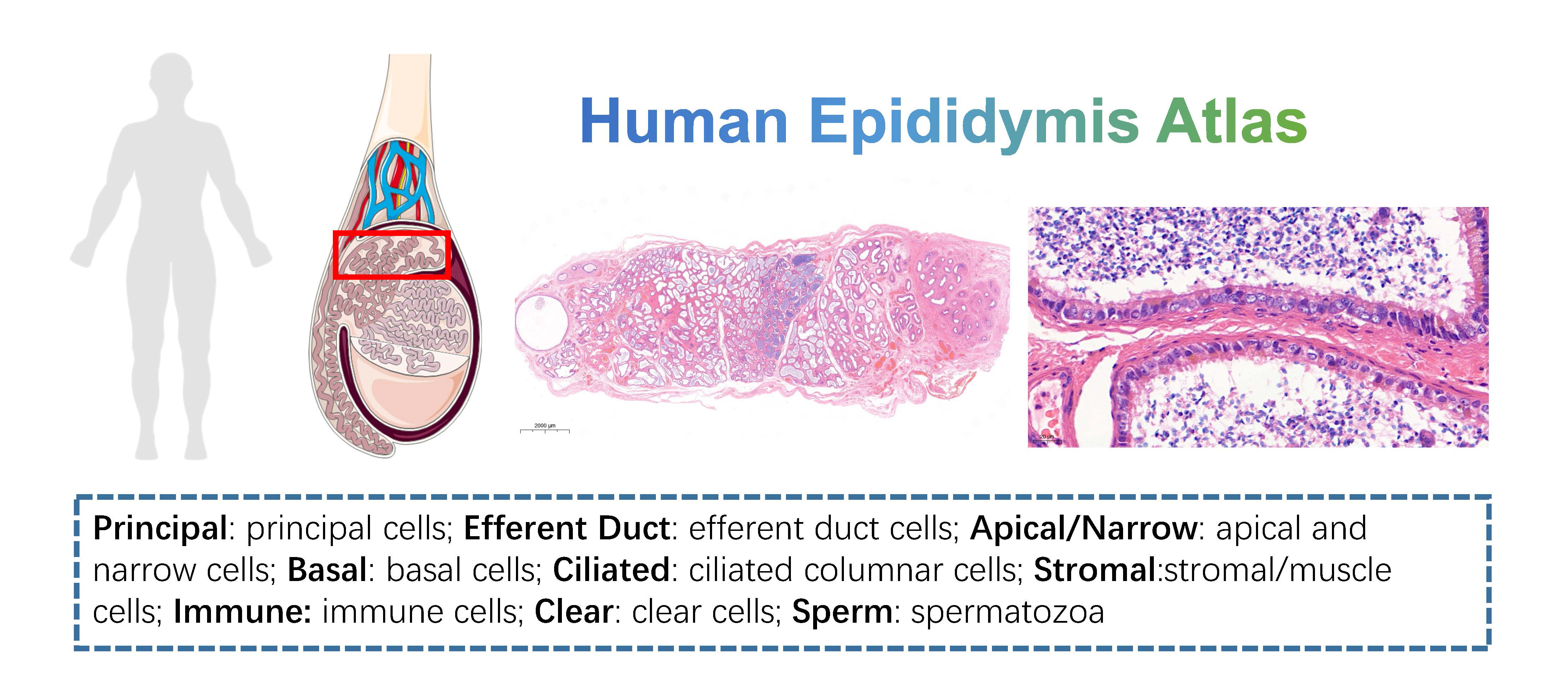
- Human Epididymis Atlas: this dataset contains 3 caput epididymidis samples from normal adult. Data could be downloaded from GSE148963 of GEO data base.
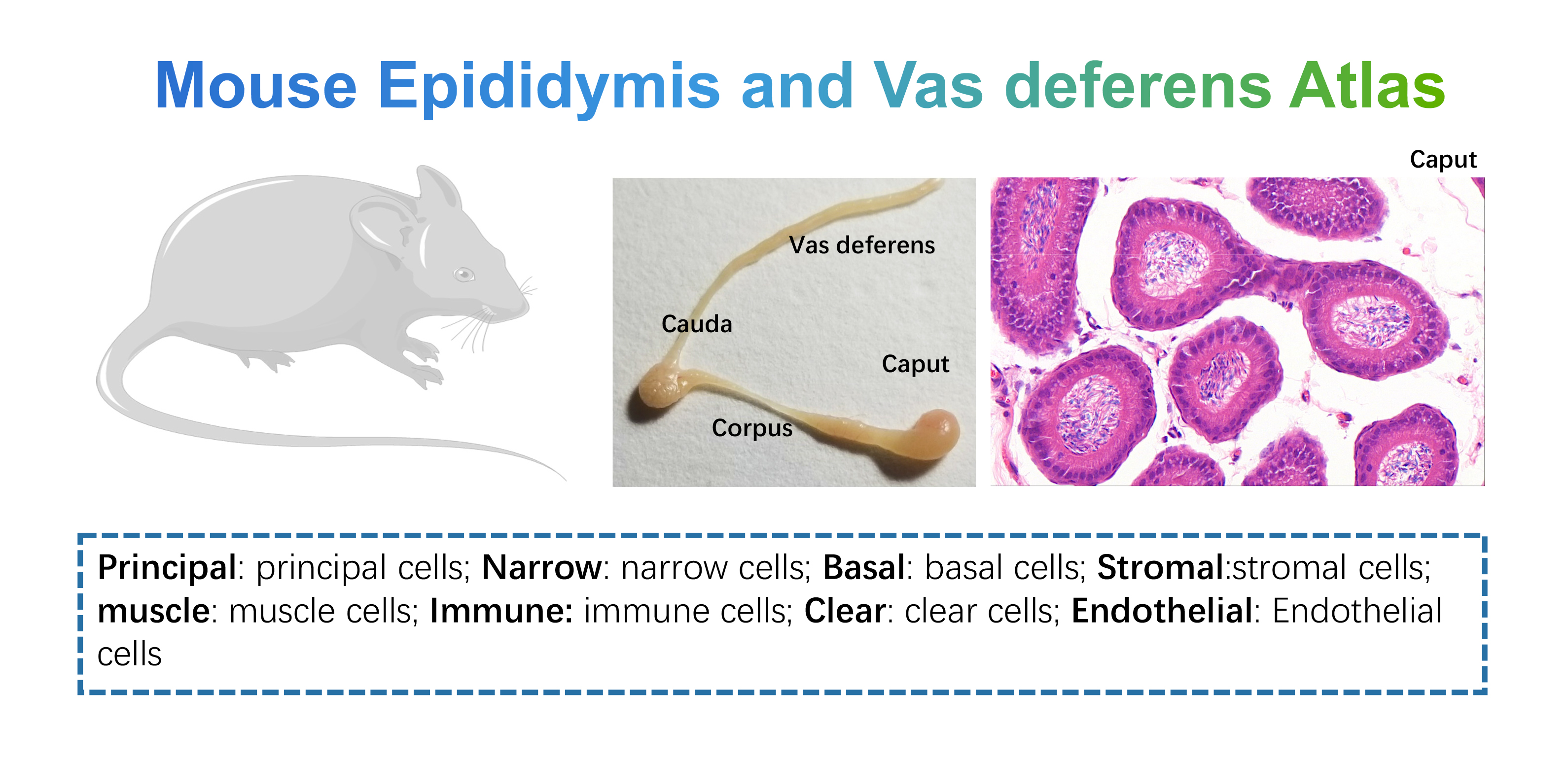
- Mouse Epididymis Vas deferens Atlas: this dataset contains samples of Caput (n=1), Cauda (n=1), Corpus (n=1), and Vas deferens (n=1) from adult mice, we provide simple and detailed clustering classifications. Data could be downloaded from GSE145443 of GEO data base.
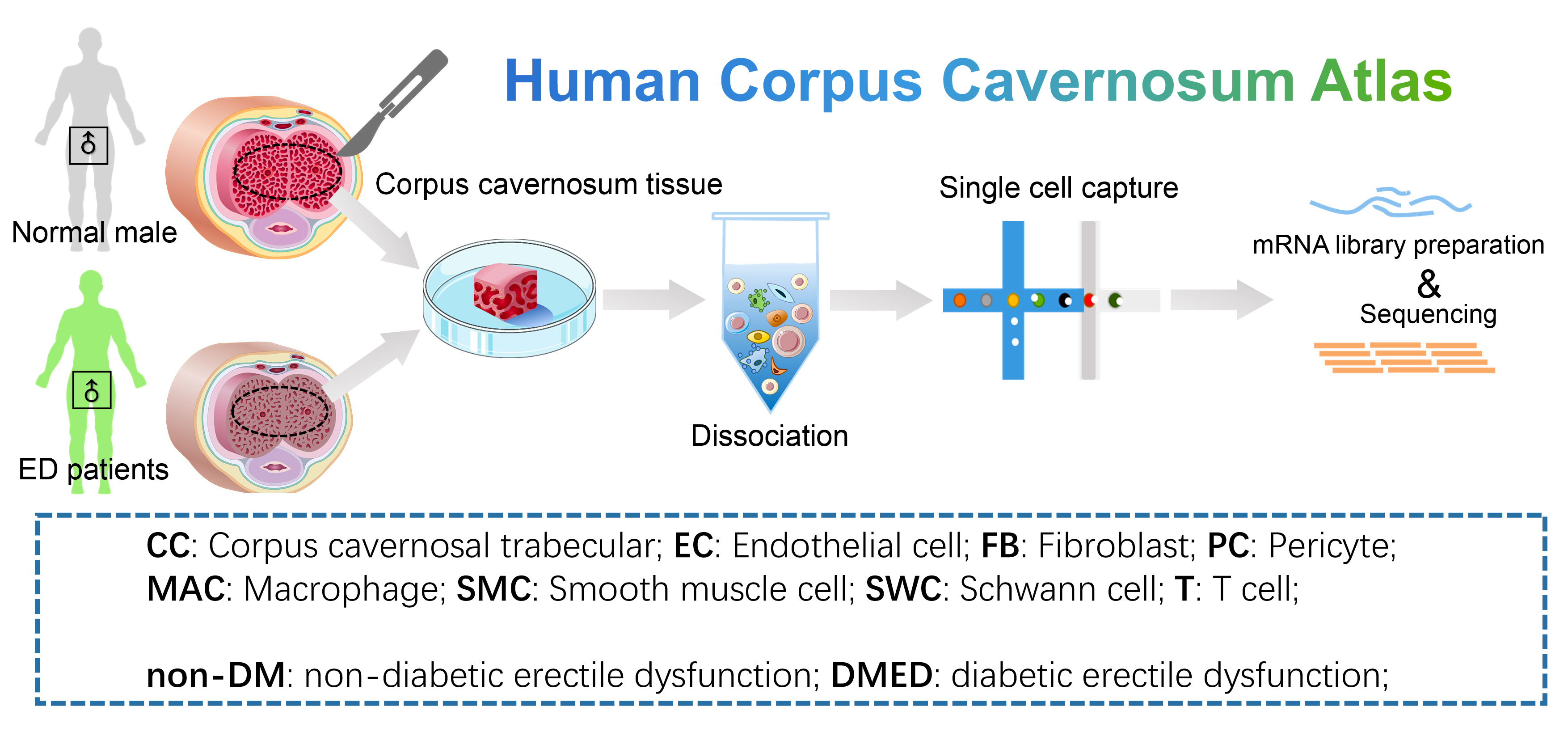
- Human Corpus Cavernosum Atlas: 8 samples of corpus cavernosum from normal men (n=3) and erectile dysfunction patients (ED, n=6). ED patients can be further classified as non-diabetic ED (non-DM, n=3) and diabetic ED (DMED, n=3). We provide simple and detailed clustering classifications. Data could be downloaded from GSE206528 and GSE259348 of GEO data base.
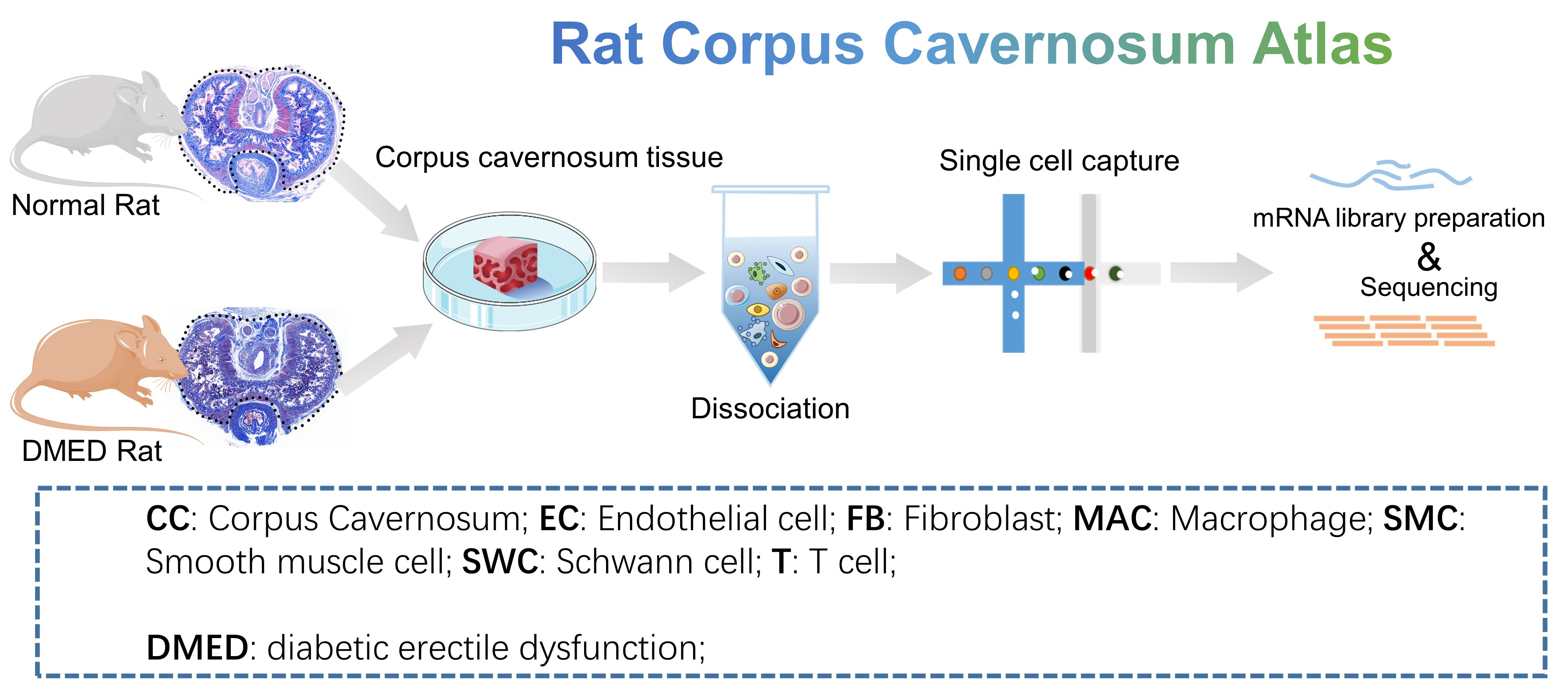
- Rat Corpus Cavernosum Atlas: 6 samples of corpus cavernosum from normal rats (normal, n=2) and diabetes mellitus erectile dysfunction rats (DMED, n=4). For the DMED rat model, streptozotocin (STZ) was injected intraperitoneally at a dose of 60 mg/kg. Corpus cavernosum tissues were collected after 4 weeks of the model was successfully established. We provide simple and detailed clustering classifications. Data could be downloaded from GSE259299 of GEO data base.
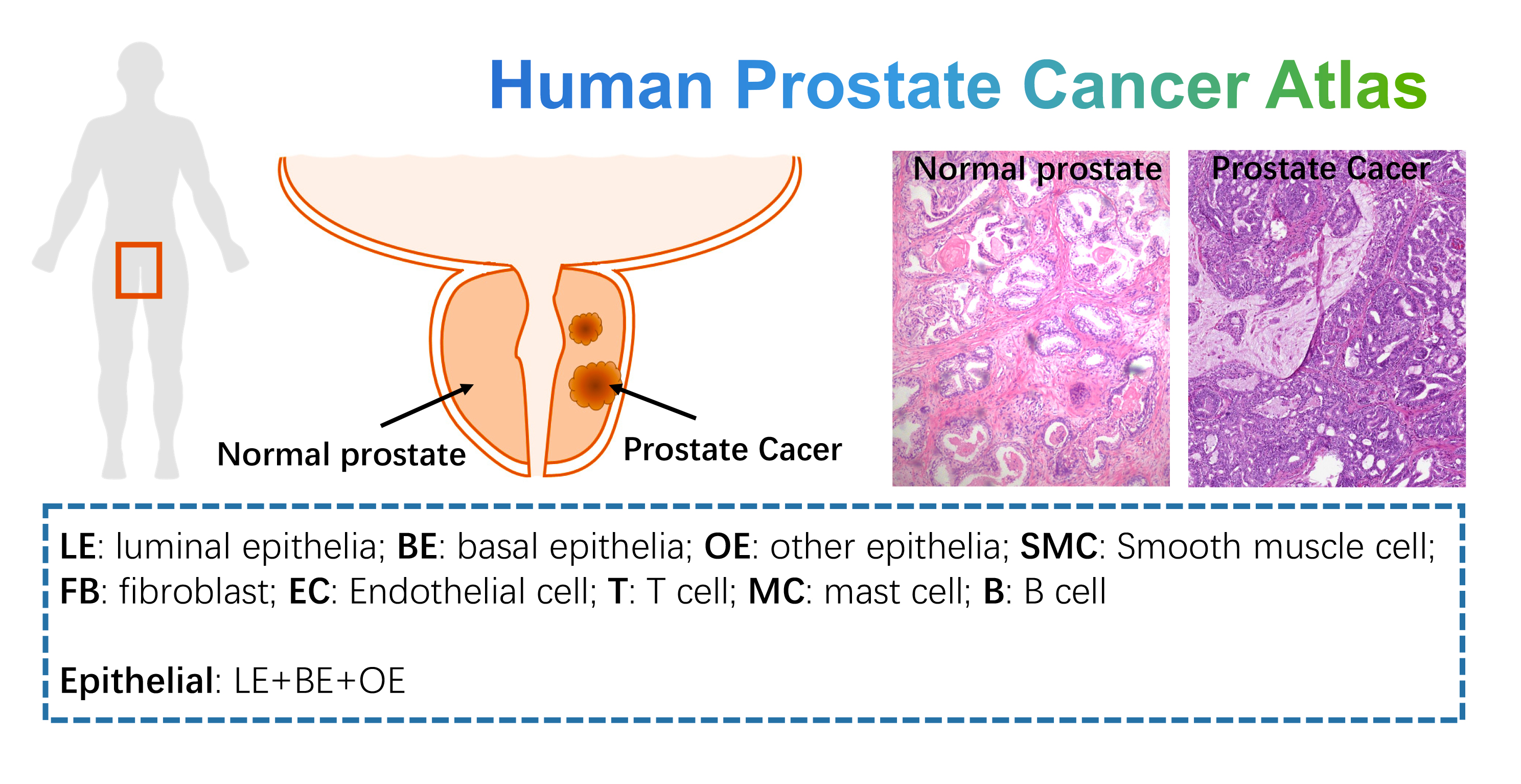
- Human Prostate Cancer Atlas: this dataset contains 19 human prostate samples from 3 normal prostates and 16 prostate cancers. We provide simple and detailed clustering classifications according to the original study description. Data could be downloaded from GSE120716 and GSE141445 of GEO data base.
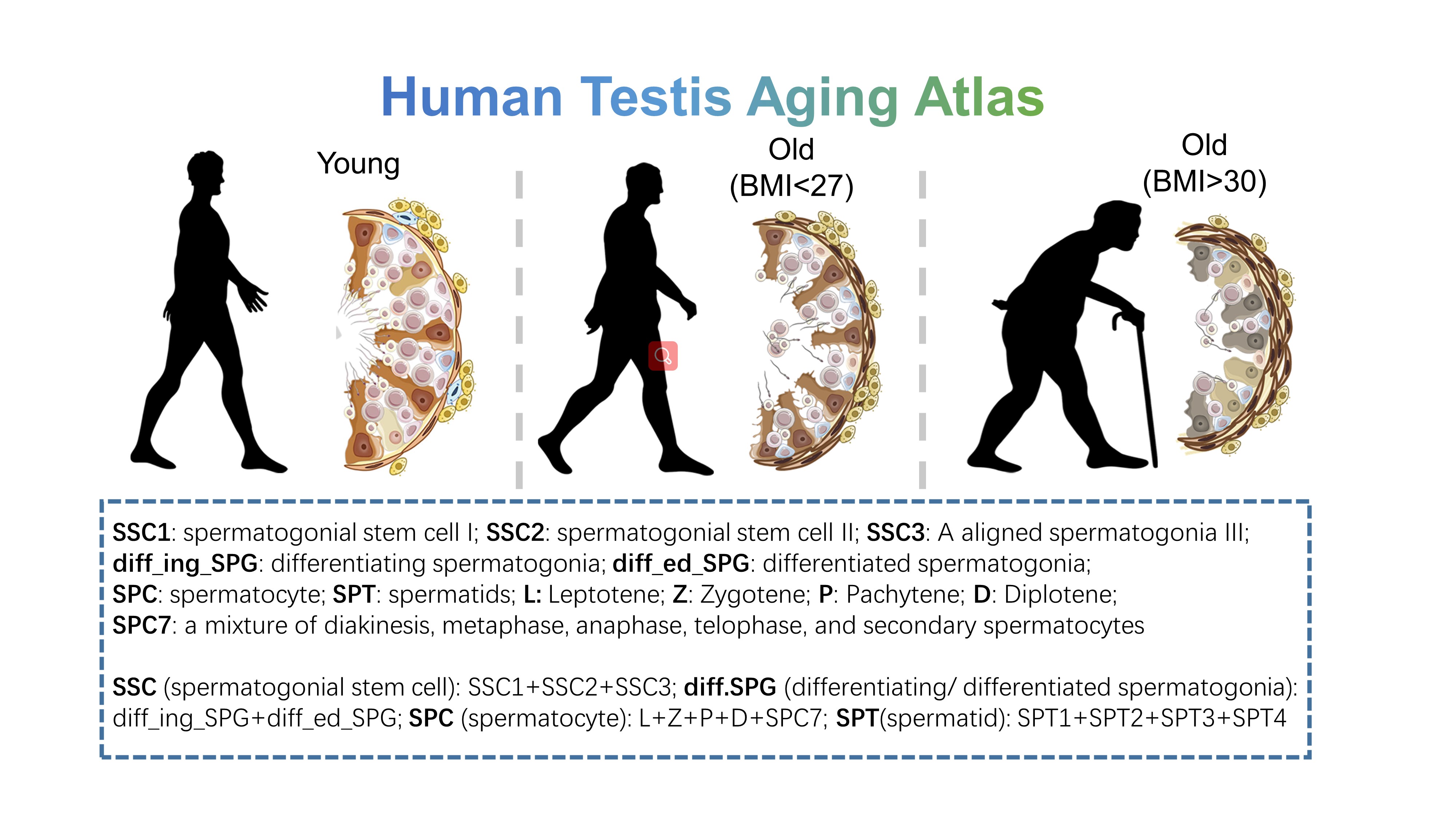
- Human Testis Aging Atlas: 12 human testicular samples include normal young (n=4), normal old (n=3) and unhealthy old (n=5, with high body mass index), to show the aging process of human testis. Data could be downloaded from GSE182786 of GEO data base.
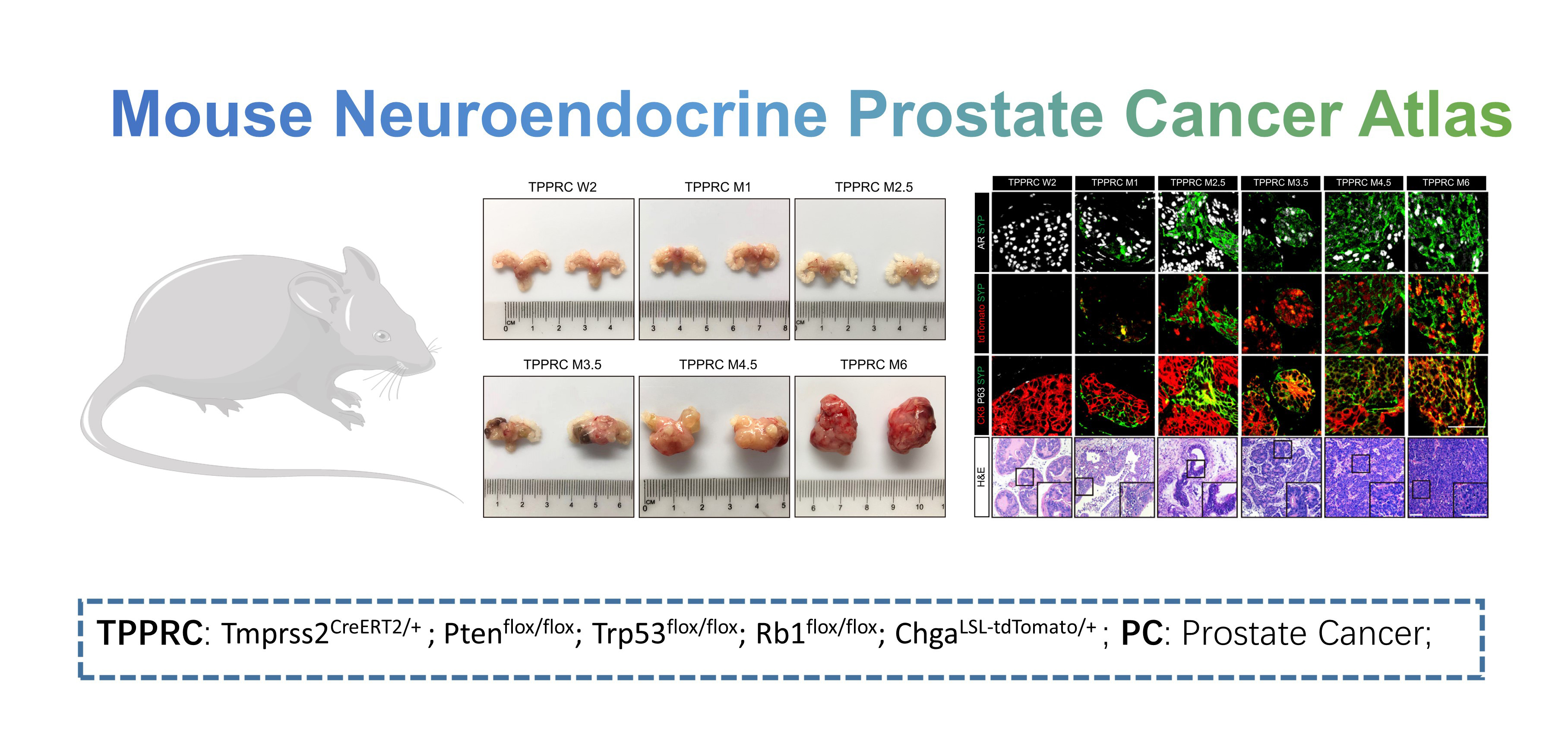
- Mouse Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Atlas: this dataset contains normal mice prostate (n=2) and prostate tumors of TPPRC mice (n2 weeks=2, n1 month=2, n2.5 month=4, n3.5 month=2, n4.5 month=2, n6 month=1) in a time-series manner post tamoxifen administration. Data could be downloaded from OMIX001928 of NGDC data base.
stRNA datasets:
Human Corpus Cavernosum: The sample is a cross-section of the corpus cavernosum from a male with normal erectile function (but suffering from a penile tumor). Due to the chip size limitation, the data only includes the middle part of one side of the corpus cavernosum. Each spot has a diameter of 50 μm. The raw data can be downloaded from GSE261085 of GEO data base.
Rat Corpus Cavernosum: The sample is a cross-section of the corpus cavernosum from a health rat at 4 months old. Each spot has a diameter of 50 μm. The raw data can be downloaded from GSE261487 of GEO data base.
News
Version: 1.1
Atlas updated: 2023-08-12
- Added a new dataset, the Mouse Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer Atlas. This dataset was gotten from OMIX: OMIX001928.
- Added a DMED sample to Human Corpus Cavernosum Atlas dataset so that it contains 3 biological repeats for normal, non-DMED and DMED, respectively.
Version: 1.2
Atlas updated: 2024-02-29
- Added a new dataset, the Rat Corpus Cavernosum Atlas. This dataset was gotten from GEO: GSE259299.
- Added a new webpage to show the spatial transcriptome data, we provide cell spatial distribution and gene expression spatial pattern plots.
Version: 2.0
Atlas updated: 2024-07-05
- Welcome to the all-new MHA. In this update, we have included stRNA data, featuring two datasets: Human Corpus Cavernosum and Rat Corpus Cavernosum, which are now available on the SPATIAL page. Feel free to explore. The previous scRNA datasets have been moved to the SINGLE-CELL page. If you would like to suggest any datasets for inclusion in MHA, please contact Dr. Zhao.
Cite
Zhao L, Zhao Y, Yao CC, Dai YB, Li Z, Tang YX.MHA, an interactive website for scRNA-seq data of male genitourinary development and disease. Andrology.
2023;1-6. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.13402
Funding
MHA is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82201756, LiangYu Zhao; and 82071636, YuXin Tang), National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC2702700, Zheng Li), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M703747, LiangYu Zhao), GuangDong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515111109, LiangYu Zhao).
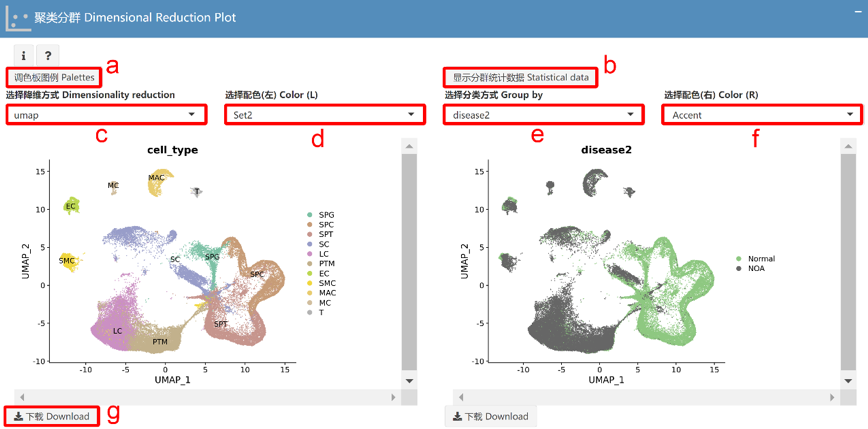
 聚类分群 Dimensional Reduction Plot
聚类分群 Dimensional Reduction Plot
 聚类分群 Dimensional Reduction Plot
聚类分群 Dimensional Reduction Plot
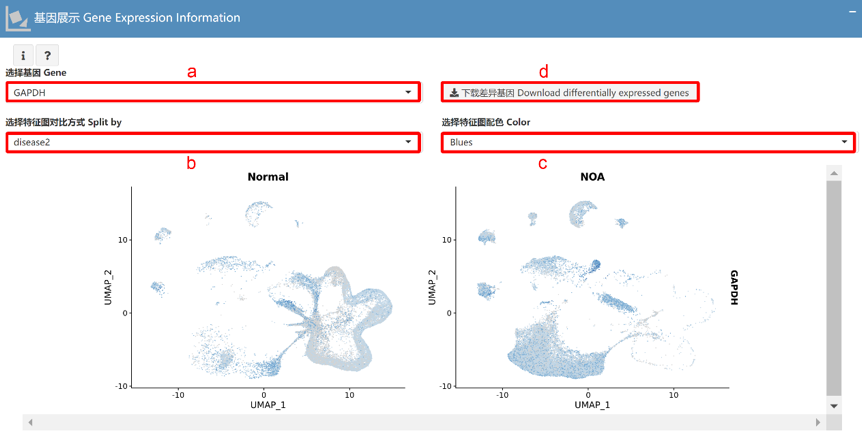
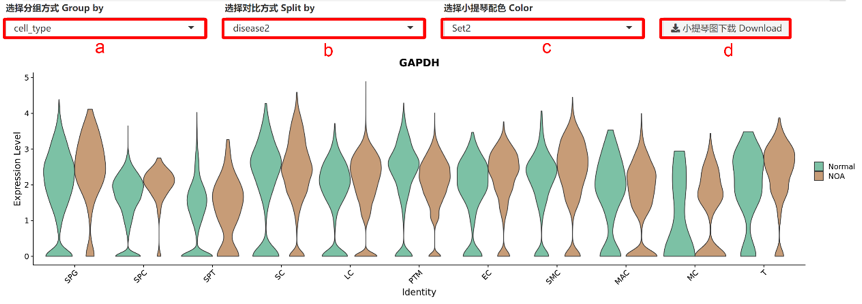
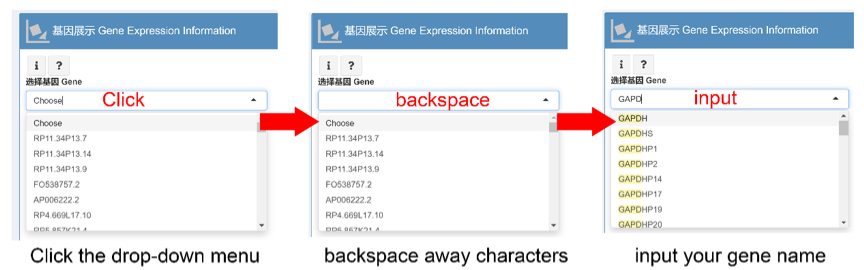
 基因展示 Gene Expression Information
基因展示 Gene Expression Information
 基因展示 Gene Expression Information
基因展示 Gene Expression Information